Have you ever paused to count the number of tech gadgets in your car, home, or office? You’d probably lose count! Imagine trying to go even an hour without interacting with technology—impossible, right? And consider this: how many businesses do you know that aren’t connected to the internet or reliant on computers? Probably none. Digital transformation began in earnest in the 1980s and has since touched every aspect of our lives, including manufacturing.
But as digital technology becomes more embedded in everything we do, confusion between three key terms—digitization, digitalization, and digital transformation—has grown. These terms might look and sound similar, but they represent distinctly different concepts. Misusing them can lead to misunderstandings, misaligned goals, and costly mistakes in business planning and communication.
In this article, we’ll dive into what each term means, how they impact manufacturing, and why using them correctly is critical.
Understanding Digitization
Digitization is the process of converting analog information into digital formats—a transformation that has evolved significantly over time. The roots of digitization stretch back to the 1700s with the invention of the first binary system, but a pivotal moment came in 1969 with the launch of the charge-coupled device (CCD). This breakthrough allowed light to be converted into digital information, paving the way for digital cameras and other imaging devices.
Examples of digitization are all around us. Think about converting paper blueprints into Computer-Aided Drafting (CAD) files, scanning sales orders into PDFs, or using 3D scanning to create digital models of physical parts. These processes typically involve transforming historical analog data into more useful and storable digital formats.

The benefits of digitization are vast:
- Blueprints to CAD:
- Storage Efficiency: A roomful of physical blueprints can be reduced to a mere slot on a computer or in cloud storage.
- Longevity: While physical blueprints deteriorate over time, digital files can last indefinitely, with future-proofing made possible by ongoing technology upgrades.
- Cost Savings: Digitization slashes costs associated with storage space, materials, air conditioning, and staff hours spent on filing and retrieval.
- Sales Orders to Database Records:
- Besides shared benefits like storage and cost savings, digitized sales orders allow detailed data analysis. For instance, you can easily track customer purchases over time, analyze part sales, and identify your most profitable products.
- 3D Scanning of Physical Parts:
- Imagine scanning a space to capture its exact dimensions. This digital data allows for precise design solutions, reducing time-to-market and cutting costs by ensuring only necessary tools are on-site during installation.
What is Digitalization?
While digitization converts analog data into digital formats, digitalization takes it a step further by using digital tools to revolutionize processes, services, and operations. Take the DMV, for example. Remember when you needed to bring proof of insurance, last year’s registration, and a checkbook for any transaction? Those days are long gone, thanks to digitalization.

- In-Person Transactions:
- No more waiting in line at the DMV. Now, you can renew your registration online from the comfort of your home. This shift to digital self-service not only reduces the DMV’s labor costs but also saves you time, allowing you to complete tasks 24/7 without disrupting your day.
- Physical Documents and Payments:
- Forget about printing out documents or writing checks. Digitalization has replaced these with automated data validation and electronic payments, boosting accuracy and streamlining the entire process.
The impact of digitalization extends beyond the DMV—it’s transforming manufacturing too. Gone are the days of paper drawings and handwritten records.
- Paper Drawings:
- In the past, manufacturing engineers relied on paper drawings to build products. Today, digitalization replaces these with CAD files displayed on screens, and manual tracking is replaced with intuitive digital interfaces.
- Process Flows:
- The journey of a product through the manufacturing process is now guided by digital tools like QR codes and barcodes. This not only ensures that each item moves efficiently through production but also provides real-time insights into operations. Manufacturers can instantly spot bottlenecks, address breakdowns, and leverage historical data for continuous improvement.
The Scope of Digital Transformation
Digital transformation is the ultimate game-changer, offering a holistic approach to reimagining an organization’s structure, processes, and strategies. Instead of merely optimizing individual tasks through digitalization, digital transformation takes a step back to examine the entire end-to-end process flow and overarching business strategies. The goal? To slash expenses, boost efficiency, and drive profitability.
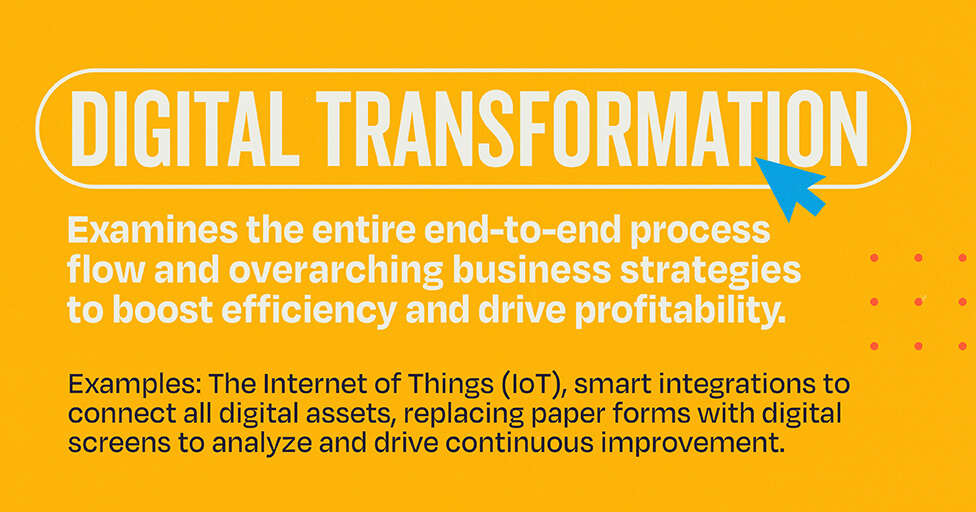
- Harnessing the Power of IoT:
- Imagine a manufacturing process where every activity is monitored in real time. The Internet of Things (IoT) enables this by collecting data across the entire production line. This data isn’t just for show—it’s analyzed to predict when maintenance is needed, preventing costly downtimes and ensuring smooth operations.
- From Paper to Pixels:
- Replacing paper forms with digital screens revolutionizes the way information is handled. Not only does this provide instant access to real-time manufacturing data, but it also creates a treasure trove of digital information. This data can be analyzed later to uncover insights and drive continuous improvement.
- Seamless Integration for Maximum Impact:
- Even the most advanced digital tools can fall short if they operate in isolation. By connecting these standalone digital assets through smart integrations, businesses can eliminate manual data entry errors and streamline operations. This synergy elevates the entire manufacturing process, driving efficiency to new heights.
Conclusion
We’ve explored how digitization, digitalization, and digital transformation, though similar, represent distinct processes that can dramatically improve how individuals and companies operate. It’s crucial to apply these concepts correctly to avoid costly mistakes and project delays.
Look at your business and manufacturing processes: where can digitization reduce costs? Where can digitalization expedite tasks? And how can digital transformation help you rethink how business is done?
For a successful digital project, be clear about your objectives, desired outcomes, and benchmarks to ensure continuity during the transformation. Remember, understanding and correctly using these terms is essential for effective communication and execution.
MBB is your strategic partner for navigating digitization, digitalization, and digital transformation. We don’t just assess what you have in place—we collaborate with you to envision and implement the innovative solutions that will drive your business forward. Let’s turn your digital potential into reality together.
Subscribe to our newsletter
Get our insights and perspectives delivered to your inbox.